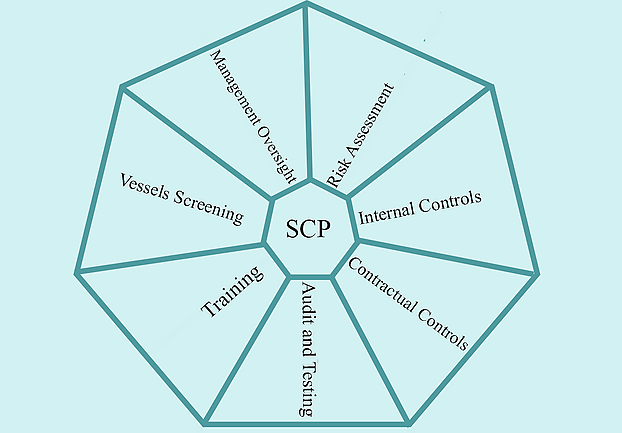
The 7 Essential Components of a Sanctions Compliance Programme
In the present period of heightened sanctions risks, there has been a massive focus on understanding what conduct is or is not permitted under Sanctions regulations.
Apart from understanding the applicable sanctions regimes, it is essential that companies design and implement adequate Sanction Compliance Programmes (SCP). The SCP will ensure that the company can comply with the relevant sanctions programmes but also meet the applicable regulator’s expectations so it can be relied upon as a mitigating factor should the ever the need arise.
Famously, OFAC has published extensive guidance with their 5 “Essential Components of Sanctions Compliance Programme". For most companies operating internationally, this generally covers the most significant risk, but does it cover the requirements of other national requirements such as the UK, EU, Switzerland and Singapore? What other elements should you take into account?
We have reviewed the guidance of the most significant jurisdictions and have distilled it into 7 principles of a successful Sanctions Compliance Programme.
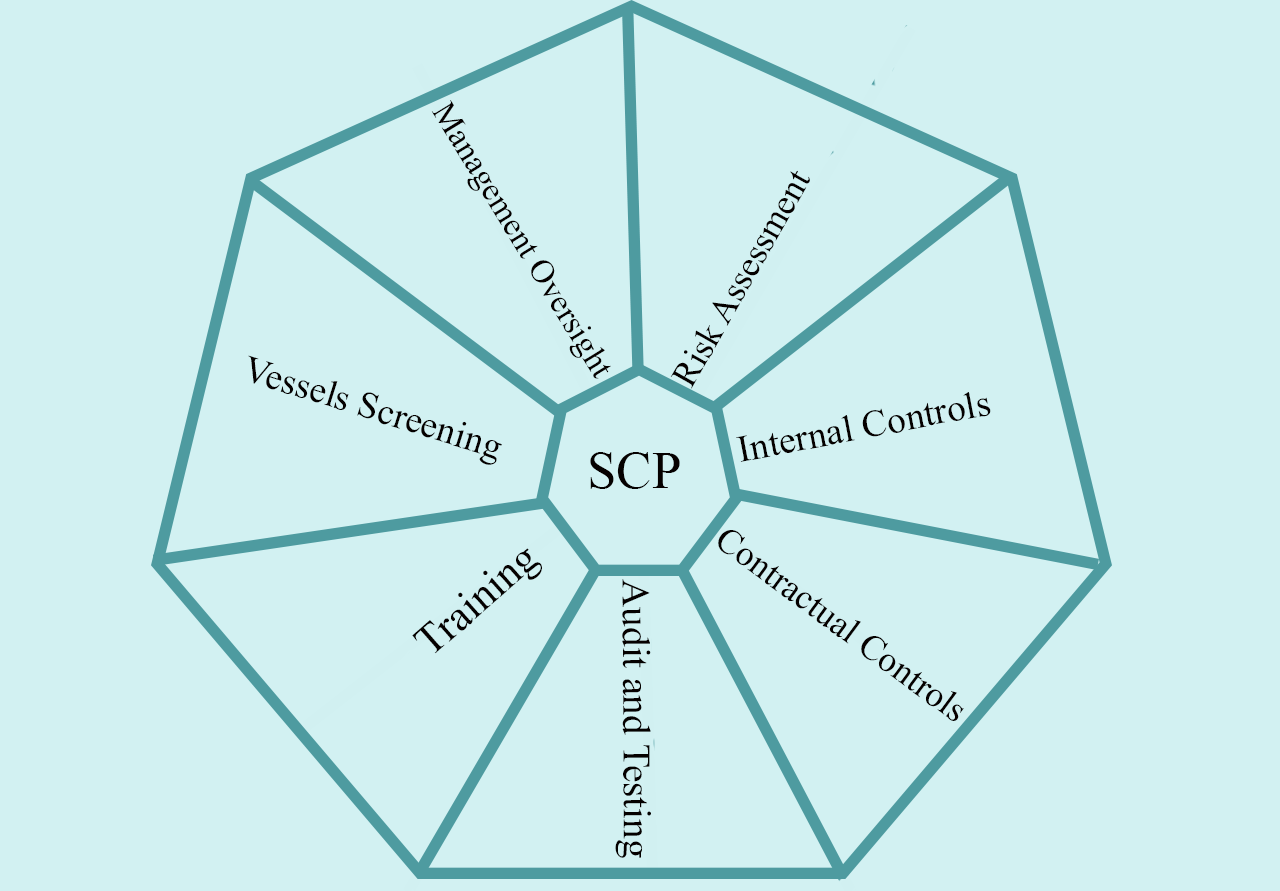
The 7 Principles: (TL;DR)
- 1- Management Oversight: management to ensure processes are followed – Make expectations very clear.
- 2- Risk Assessment: map business flows, risks, and mitigants – Ensure a fit-for-purpose SCP.
- 3- Internal Controls: Internal controls need to be proportionate to the risks – Proportionate controls managed by experienced staff.
- 4- Contractual Controls: clauses to allow exiting any transaction if it would cause a breach – Clear contractual prohibitions showing your intent.
- 5- Audit and Testing: regular independent internal scrutiny to assess the effectiveness of processes – Assurance of an effective SCP.
- 6- Training: ensure that the SCP is well implemented and understood by all within the company – Make sure staff is versed in the SCP.
- 7- Vessels Red Flag Screening: have specific procedures to monitor constantly the vessels used – Ensure your supply chain.
The 7 Essential Components of an SCP:
Most companies generally rely upon the 5 Components as advocated by OFAC, but companies wanting to ensure their SCP covers broader requirements should, in reality, consider 7 core elements to their SCP:
1- Management Oversight:
All guidance is unanimous that Senior Management and ‘Tone from the Top’ is crucial to an SCP. In addition, management expectations, company policies and associated processes, responsibilities and escalation channels must be clearly defined and implemented.
Senior management is responsible for ensuring that staff allocated to these tasks has the required resources and authority to undertake their duty correctly.
Checklist for implementing sound management oversight:
-> Has senior management reviewed and approved the programme, including receiving regular management reporting on Sanction Compliance activities?
-> Have control staff been delegated sufficient authority to undertake their duties?
-> Ensure that the controls have sufficient resources, including that relevant staff have the required expertise and knowledge to conduct their controls.
-> Does senior management promote a culture of Compliance?
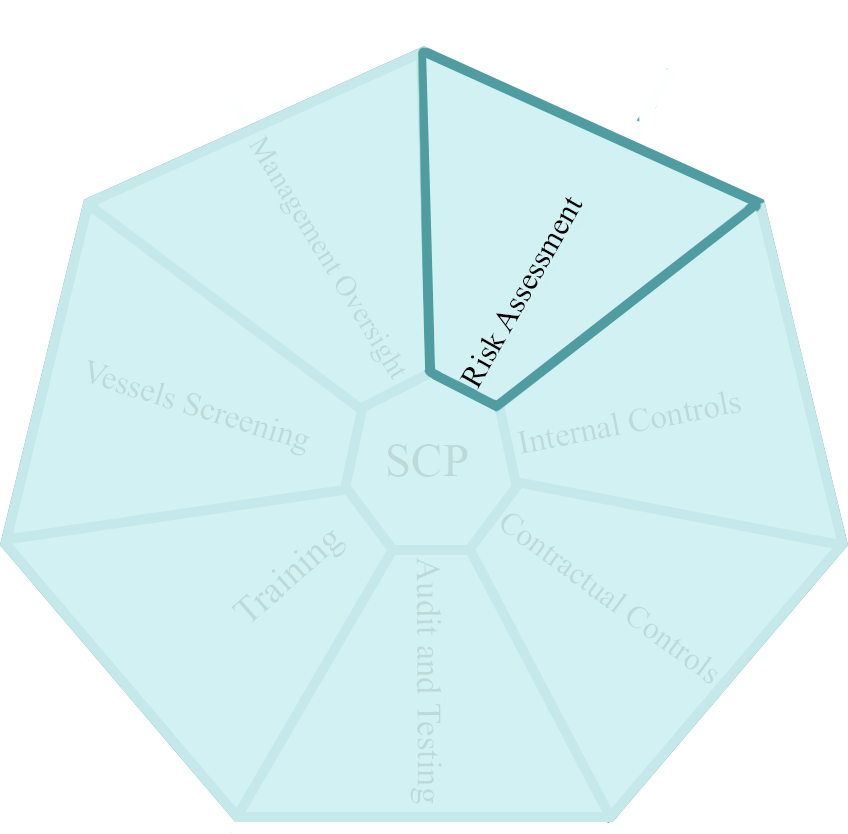
2- Risk Assessment:
Often overlooked, one of the essential elements of a fit-for-purpose SCP is the Risk Assessment. Mapping business flows and identifying risks and mitigants ensures that the SCP is proportional to the company's risk.
The Risk Assessment also helps document the reasons for certain decisions taken. Therefore, companies must ensure that Risk Assessments are regularly reviewed and are updated if any elements are changed, for example, by adding new businesses, products, or markets.
Checklist for a successful risk assessment:
-> A risk map of all business flows, including products, service offerings, networks, client types, supply chains and intermediaries, with a review of the relevant sanctions risk.
-> Compare your risk assessment against the OFAC Risk Matrix. Are they aligned?
-> The geographical location of the organisation and clients/customers/ suppliers
-> Is the Risk Assessment aligned with the risks?
-> How frequently is the Risk Assessment refreshed?
-> Companies should have processes to keep the risk map up to date at all times. For example, changes to the company's activities or sanctions should be noted in the Risk map when they occur.
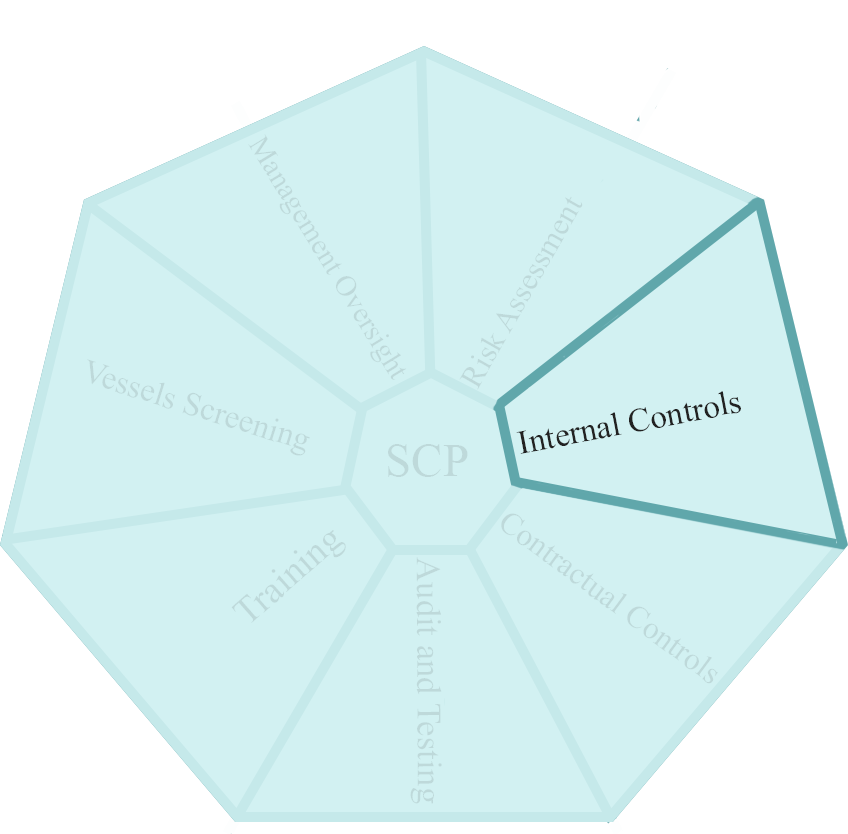
3- Internal Controls:
Internal controls need to be proportionate to the risks, with clear objectives. Internal controls must also be realistic and achievable to provide the required risk management, and companies must ensure that sufficiently experienced staff manage them.
Companies should pay particular attention to Due Diligence procedures to ensure they are complete, including frequency of screening and exception escalation and resolution. Although not a separate element, most enforcement action is based upon a failure of due diligence processes to identify, escalate and react to risks.
Checklist for relevant internal controls:
-> Do you have a Due Diligence and onboarding process that screens for Sanctions?
-> How frequently are all relevant onboarded counterparties screened for Sanctions?
-> Do you have an effective process to identify, investigate and resolve Sanctions alerts?
4- Contractual Controls:
An essential element in an SCP is the Contractual controls that companies have in place.
Contractual clauses should allow a company to exit any transaction if it would unwittingly cause a breach of sanctions. Conversely, relying on Force Majeure or Illegality clauses will rarely allow you to terminate cleanly and apply the sanctions regimes that are relevant to you.
A consistent approach should be taken for all businesses but considering differences between each type of business. Think about regimes and situations that you want to apply in all cases. A well-drafted sanctions clause will also help articulate clearly the purpose to counterparties and regulators.
Checklist to draft practical sanctions clauses:
-> What are the sanctions regimes that apply to your company globally?
-> Is your clause adequately identifying the sanctions regimes and provides for a clear termination right?
-> Is there an industry standard clause for your line of business, and how does your clause differ from it?
5- Vessels Red Flag Screening:
Companies that regularly affreight vessels need specific procedures to monitor vessels used in transactions.
Companies should identify lists of red flags such as risks of STS, Vessels operating in high-risk areas (yellow sea, for example) and how the company will monitor those risks. The US State Department and OFSI have provided guidance on red flags to incorporate into any SCP.
Checklist for Vessel Red Flag Screening:
-> Have suitable Vessel Due diligence processes to identify ownership and any irregularities which could be a red flag.
-> Vessel tracking is muchly vaunted, but in most cases, this is either not necessary or possible, but reviewing historical vessel movements can be an excellent indicator of issues to investigate further such as AIS blackholes or STS in unusual locations.
6- Audit and Testing:
How does a company ensure that its controls are adequate and fit for purpose? Audit and testing provide a demonstrable review of control effectiveness. The results, however, must go back into risk assessments, policies and procedures.
Checklist for Audit and Testing:
-> Is your SCP regularly tested by an independent function or advisors?
-> Are the findings and recommendations presented to senior management?
-> Are remedial actions followed up and completed?
7- Training:
Finally training. How does the company ensure that its well-thought-out SCP is well implemented and understood by all within the company other than through regular training?
Training should be risk-based to ensure that the most resources are spent on training those who look after the highest risks or have direct responsibilities.
Checklist for Training:
-> Do you have regular training on SCP policies and procedures?
-> Does training reflect lessons learnt from enforcement action?
The importance of documenting decisions:
It is essential that companies actively document decisions to be able to demonstrate what factors lead to the decisions taken and, more importantly, their links to the company’s Risk Assessment.
Guidance from Authorities generally mentions “risked based” and “proportionate” when referring to companies' SCP, which can affect different elements of the SCP, from resourcing to due diligence policies and requirements.
But what does this mean, and how can a company ensure that what it believes is proportional is in sync with an Authority's view? In the context of an SCP, proportionate depends squarely on a company’s risk assessment. But this doesn’t mean a company is isolated from errors or mistakes that could lead to inadvertent breaches.
Therefore, companies must actively document decisions to demonstrate what factors lead to the decisions being taken and links to the company’s Risk Assessment.

How Sybius Consulting can help:
At Sybius Consulting we have a combined 30+ years of first-hand experience managing sanctions risk within trading environments. We can provide our experience in helping draft an optimised Sanctions Compliance Program or ensure that your existing policy and controls meet relevant standards, reducing your Sanctions risks.
Who we are:
A boutique consultancy company focused on guiding companies in the Commodity Trading and Financial Markets community to navigate the regulatory and legal landscape. We leverage our extensive experience to simplify and create robust risk frameworks that integrate effortlessly with your Company’s business needs.
For more information please contact us: INFO@SYBIUSCONSULTING.COM
This article was published by Sybius in LinkedIn: click here to access
For more articles like this one, follow us on LinkedIn